go smtp实现邮件发送示例详解
来源:脚本之家
2022-12-30 16:19:24
0浏览
收藏
在Golang实战开发的过程中,我们经常会遇到一些这样那样的问题,然后要卡好半天,等问题解决了才发现原来一些细节知识点还是没有掌握好。今天golang学习网就整理分享《go smtp实现邮件发送示例详解》,聊聊gosmtp、邮件发送,希望可以帮助到正在努力赚钱的你。
smtp指令
书接上文邮件实现详解,这里我们及我们简单复习一下smtp的指令如下:
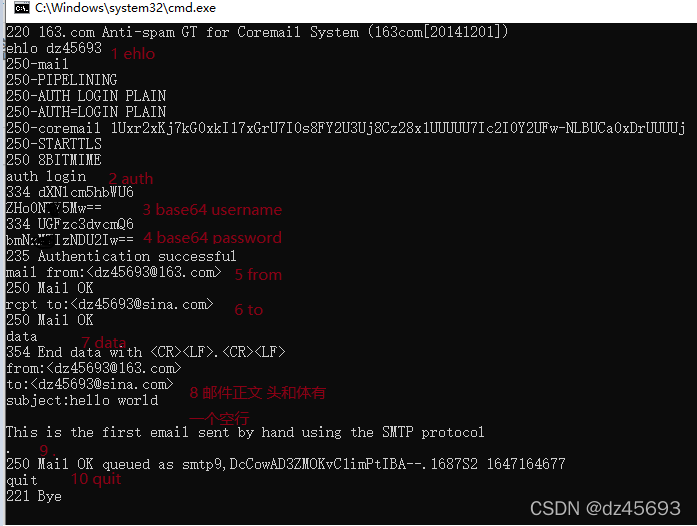
telnet smtp.163.com 25 [outpout] ehlo dz45693 [outpout] auth login [outpout] 输入用户名base64 [outpout] 输入密码base64 mail from:<dz45693> [outpout] rcpt to:<dz45693> [outpout] data [outpout] from:<dz45693> to:<dz45693> subject:hello world This is the first email sent by hand using the SMTP protocol quit </dz45693></dz45693></dz45693></dz45693>
go demo
好,那我们下现在用go实现代码让如下:这里只是一个demo,主要熟悉smtp命令
package main
import (
"bufio"
"encoding/base64"
"fmt"
"net"
"strconv"
"strings"
)
func main() {
testSmtp()
}
var gConn net.Conn
var gRead *bufio.Reader
var gWrite *bufio.Writer
//可以放到这样的类里
type TcpClient struct {
Conn net.Conn
Read *bufio.Reader
Write *bufio.Writer
} //
func Connect(host string, port int) (net.Conn, *bufio.Reader, *bufio.Writer) {
addr := host + ":" + strconv.Itoa(port)
conn, err := net.Dial("tcp", addr)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, nil
}
reader := bufio.NewReader(conn)
writer := bufio.NewWriter(conn)
return conn, reader, writer
} //
//收取一行,可再优化
func RecvLine() string {
line, err := gRead.ReadString('\n') //如何设定超时?
if err != nil {
fmt.Print(err)
return ""
}
line = strings.Split(line, "\r")[0] //还要再去掉 "\r",其实不去掉也可以
return line
}
func SendLine(line string) {
gWrite.WriteString(line + "\r\n")
gWrite.Flush()
}
//解码一行命令,这里比较简单就是按空格进行分隔就行了
func DecodeCmd(line string, sp string) []string {
tmp := strings.Split(line, sp)
var cmds = []string{"", "", "", "", ""} //先定义多几个,以面后面使用时产生异常
for i := 0; i = len(cmds) {
break
}
cmds[i] = tmp[i]
}
return cmds
}
//读取多行结果
func RecvMCmd() string {
i := 0
rs := ""
mLine := ""
for i = 0; i <domain><crlf>
//收取多行
line = RecvMCmd()
fmt.Println("recv:" + line)
//--------------------------------------------------
//用 base64 登录
SendLine("AUTH LOGIN")
//收取一行
line = RecvLine()
fmt.Println("recv:" + line)
s := "dz45693" //要换成你的用户名,注意 163 邮箱的话不要带后面的 @域名 部分
s = base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString([]byte(s))
SendLine(s)
//收取一行
line = RecvLine()
fmt.Println("recv:" + line)
s = "xxxxx" //要换成您的密码
s = base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString([]byte(s))
SendLine(s)
//收取一行
line = RecvLine()
fmt.Println("recv:" + line)
//--------------------------------------------------
//邮件内容
from := "dz45693@163.com"
to := "dz45693@sina.com"
SendLine("MAIL FROM: ") //注意"")
//收取一行
line = RecvLine()
fmt.Println("recv:" + line)
SendLine("DATA")
//收取一行
line = RecvLine()
fmt.Println("recv:" + line)
//发送邮件头
SendLine("from:<dz45693>")
SendLine("to:<dz45693>")
SendLine("subject:hello world")
SendLine("") //发送空行 后面就是邮件体
SendLine("This is the first email sent by hand using the SMTP protocol")
SendLine(".") //邮件结束符
//收取一行
line = RecvLine()
fmt.Println("recv:" + line)
SendLine("quit") //链接推出
line = RecvLine()
fmt.Println("recv:" + line)
} //</dz45693></dz45693></crlf></domain>
运行结果如下:
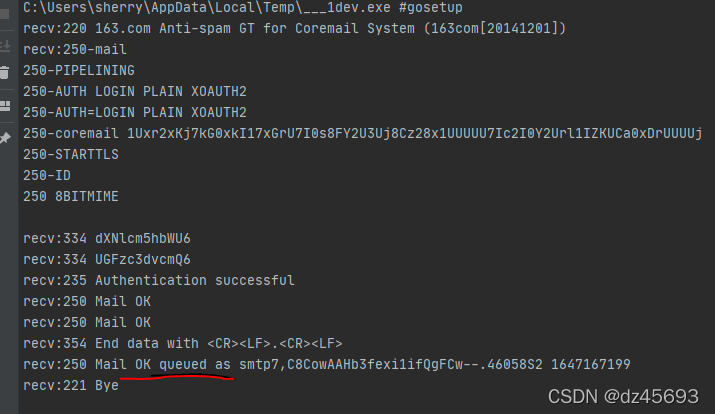
sdk中SendMail方法
在go的sdk中提供了SendMail方法【发送邮件后这个方法会关闭链接】,实现如下:
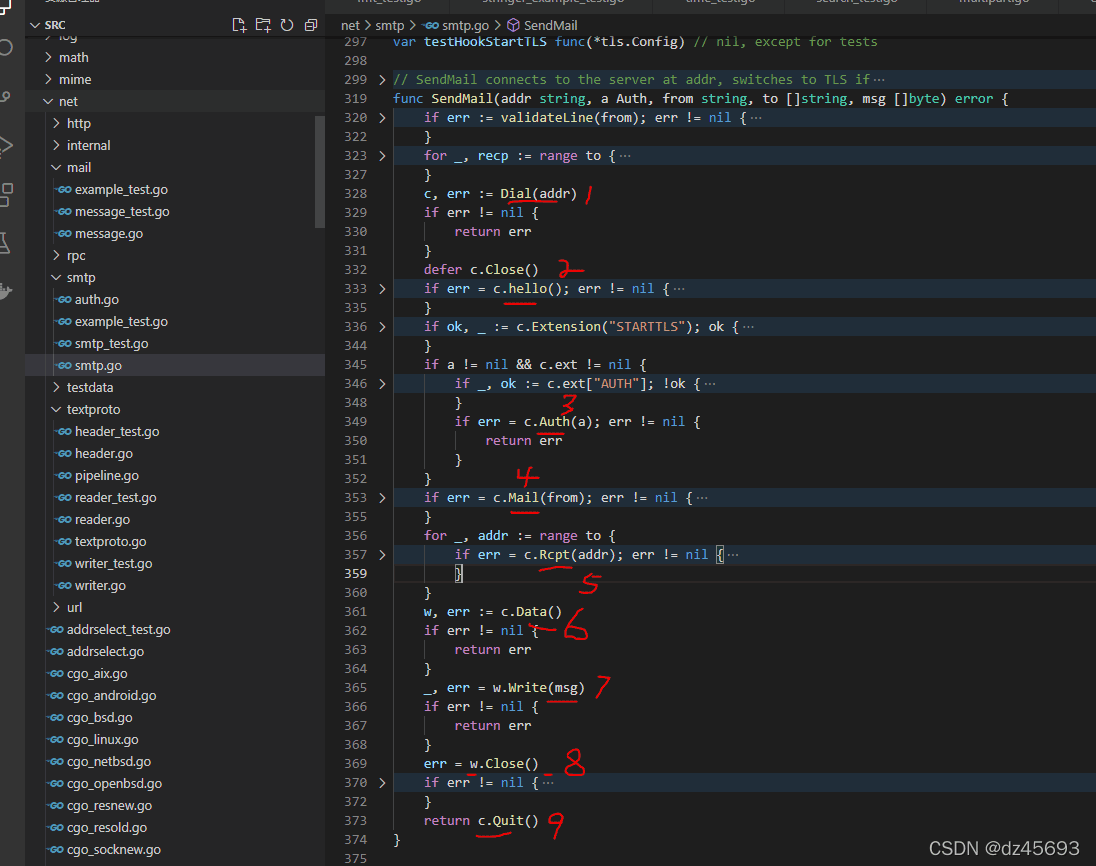
实现如下:
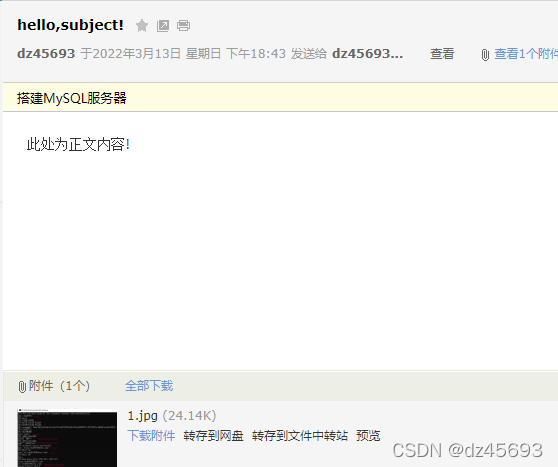
func SendMailBySmtp(){
auth := smtp.PlainAuth("", "dz45693@163.com", "xxx", "smtp.163.com")
to := []string{"dz45693@sina.com"}
image,_:=ioutil.ReadFile("d:\\Downloads\\1.png")
imageBase64:=base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(image)
msg := []byte("from:dz45693@163.com\r\n"+
"to: dz45693@sina.com\r\n" +
"Subject: hello,subject!\r\n"+
"Content-Type:multipart/mixed;boundary=a\r\n"+
"Mime-Version:1.0\r\n"+
"\r\n" +
"--a\r\n"+
"Content-type:text/plain;charset=utf-8\r\n"+
"Content-Transfer-Encoding:quoted-printable\r\n"+
"\r\n"+
"此处为正文内容!\r\n"+
"--a\r\n"+
"Content-type:image/jpg;name=1.jpg\r\n"+
"Content-Transfer-Encoding:base64\r\n"+
"\r\n"+
imageBase64+"\r\n"+
"--a--\r\n")
err := smtp.SendMail("smtp.163.com:25", auth, "dz45693@163.com", to, msg)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}
运行效果:
使用第三方库gomail实现邮件的发送更多了解,
请前往:https://pkg.go.dev/gopkg.in/gomail.v2?utm_source=godoc
示例如下:
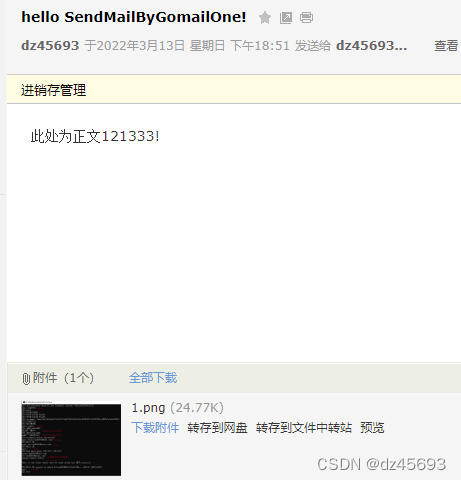
func SendMailByGomailOne(){
m := gomail.NewMessage()
m.SetAddressHeader("From", "dz45693@163.com", "dz45693")
m.SetHeader("To", "dz45693@sina.com")
m.SetHeader("Subject", "hello SendMailByGomailOne!")
m.Embed("d:\\Downloads\\1.png")
m.SetBody("text/html", "此处为正文121333!")
d := gomail.NewDialer("smtp.163.com", 25, "dz45693@163.com", "xxxx")
if err := d.DialAndSend(m); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
运行结果:
DialAndSend实现
来我们看看DialAndSend的实现如下:
package gomail
import (
"crypto/tls"
"fmt"
"io"
"net"
"net/smtp"
"strings"
"time"
)
// A Dialer is a dialer to an SMTP server.
type Dialer struct {
// Host represents the host of the SMTP server.
Host string
// Port represents the port of the SMTP server.
Port int
// Username is the username to use to authenticate to the SMTP server.
Username string
// Password is the password to use to authenticate to the SMTP server.
Password string
// Auth represents the authentication mechanism used to authenticate to the
// SMTP server.
Auth smtp.Auth
// SSL defines whether an SSL connection is used. It should be false in
// most cases since the authentication mechanism should use the STARTTLS
// extension instead.
SSL bool
// TSLConfig represents the TLS configuration used for the TLS (when the
// STARTTLS extension is used) or SSL connection.
TLSConfig *tls.Config
// LocalName is the hostname sent to the SMTP server with the HELO command.
// By default, "localhost" is sent.
LocalName string
}
// NewDialer returns a new SMTP Dialer. The given parameters are used to connect
// to the SMTP server.
func NewDialer(host string, port int, username, password string) *Dialer {
return &Dialer{
Host: host,
Port: port,
Username: username,
Password: password,
SSL: port == 465,
}
}
// NewPlainDialer returns a new SMTP Dialer. The given parameters are used to
// connect to the SMTP server.
//
// Deprecated: Use NewDialer instead.
func NewPlainDialer(host string, port int, username, password string) *Dialer {
return NewDialer(host, port, username, password)
}
// Dial dials and authenticates to an SMTP server. The returned SendCloser
// should be closed when done using it.
func (d *Dialer) Dial() (SendCloser, error) {
conn, err := netDialTimeout("tcp", addr(d.Host, d.Port), 10*time.Second)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if d.SSL {
conn = tlsClient(conn, d.tlsConfig())
}
c, err := smtpNewClient(conn, d.Host)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if d.LocalName != "" {
if err := c.Hello(d.LocalName); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
if !d.SSL {
if ok, _ := c.Extension("STARTTLS"); ok {
if err := c.StartTLS(d.tlsConfig()); err != nil {
c.Close()
return nil, err
}
}
}
if d.Auth == nil && d.Username != "" {
if ok, auths := c.Extension("AUTH"); ok {
if strings.Contains(auths, "CRAM-MD5") {
d.Auth = smtp.CRAMMD5Auth(d.Username, d.Password)
} else if strings.Contains(auths, "LOGIN") &&
!strings.Contains(auths, "PLAIN") {
d.Auth = &loginAuth{
username: d.Username,
password: d.Password,
host: d.Host,
}
} else {
d.Auth = smtp.PlainAuth("", d.Username, d.Password, d.Host)
}
}
}
if d.Auth != nil {
if err = c.Auth(d.Auth); err != nil {
c.Close()
return nil, err
}
}
return &smtpSender{c, d}, nil
}
func (d *Dialer) tlsConfig() *tls.Config {
if d.TLSConfig == nil {
return &tls.Config{ServerName: d.Host}
}
return d.TLSConfig
}
func addr(host string, port int) string {
return fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d", host, port)
}
// DialAndSend opens a connection to the SMTP server, sends the given emails and
// closes the connection.
func (d *Dialer) DialAndSend(m ...*Message) error {
s, err := d.Dial()
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer s.Close()
return Send(s, m...)
}
type smtpSender struct {
smtpClient
d *Dialer
}
func (c *smtpSender) Send(from string, to []string, msg io.WriterTo) error {
if err := c.Mail(from); err != nil {
if err == io.EOF {
// This is probably due to a timeout, so reconnect and try again.
sc, derr := c.d.Dial()
if derr == nil {
if s, ok := sc.(*smtpSender); ok {
*c = *s
return c.Send(from, to, msg)
}
}
}
return err
}
for _, addr := range to {
if err := c.Rcpt(addr); err != nil {
return err
}
}
w, err := c.Data()
if err != nil {
return err
}
if _, err = msg.WriteTo(w); err != nil {
w.Close()
return err
}
return w.Close()
}
func (c *smtpSender) Close() error {
return c.Quit()
}
// Stubbed out for tests.
var (
netDialTimeout = net.DialTimeout
tlsClient = tls.Client
smtpNewClient = func(conn net.Conn, host string) (smtpClient, error) {
return smtp.NewClient(conn, host)
}
)
type smtpClient interface {
Hello(string) error
Extension(string) (bool, string)
StartTLS(*tls.Config) error
Auth(smtp.Auth) error
Mail(string) error
Rcpt(string) error
Data() (io.WriteCloser, error)
Quit() error
Close() error
}
DialAndSend ,首先调用Dial方法创建连接,然后发送邮件,最后关闭链接,如果要频繁发邮件,那么是否保持长连接更好了?这里的Dial 调用了smtp.NewClient 创建smtp.Client对象c,然后调用c.Hello ,c.Auth,send 实际是调用c.Mail,c.Rcpt,c.Data,那么我们可以自己调用Dial方法 然后循环调用send方法,最后在close。
代码如下:
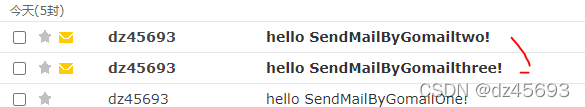
func SendMailByGomailTwo() {
d := gomail.NewDialer("smtp.163.com", 25, "dz45693@163.com", "xxxx")
m := gomail.NewMessage()
m.SetAddressHeader("From", "dz45693@163.com", "dz45693")
m.SetHeader("To", "dz45693@sina.com")
m.SetHeader("Subject", "hello SendMailByGomailtwo!")
m.Embed("d:\\Downloads\\1.png")
m.SetBody("text/html", "此处为正文121333!SendMailByGomailtwo")
s, err := d.Dial()
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer s.Close()
err = gomail.Send(s, m)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
m.Reset()
m.SetAddressHeader("From", "dz45693@163.com", "dz45693")
m.SetHeader("To", "dz45693@sina.com")
m.SetHeader("Subject", "hello SendMailByGomailthree!")
m.Embed("d:\\Downloads\\2.png")
m.SetBody("text/html", "此处为正文1SendMailByGomailthreeSendMailByGomailthree!")
err = gomail.Send(s, m)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
运行结果:
到这里,我们也就讲完了《go smtp实现邮件发送示例详解》的内容了。个人认为,基础知识的学习和巩固,是为了更好的将其运用到项目中,欢迎关注golang学习网公众号,带你了解更多关于golang的知识点!
版本声明
本文转载于:脚本之家 如有侵犯,请联系study_golang@163.com删除
 Go语言入门exec的基本使用示例
Go语言入门exec的基本使用示例
- 上一篇
- Go语言入门exec的基本使用示例
- 下一篇
- go GCM gin中间件的加密解密文件流处理
查看更多
最新文章
-

- Golang · Go教程 | 1分钟前 |
- GolangI/O优化技巧与实战方法
- 115浏览 收藏
-

- Golang · Go教程 | 4分钟前 |
- Golang服务如何开启Prometheus监控指标
- 142浏览 收藏
-

- Golang · Go教程 | 5分钟前 |
- Go字符串不区分大小写比较方法
- 123浏览 收藏
-

- Golang · Go教程 | 7分钟前 |
- Gostruct映射动态JSON实战技巧
- 185浏览 收藏
-

- Golang · Go教程 | 10分钟前 |
- Gosum作用及使用解析
- 428浏览 收藏
-

- Golang · Go教程 | 16分钟前 |
- Golang性能测试与优化技巧
- 187浏览 收藏
-

- Golang · Go教程 | 30分钟前 |
- Golang性能测试对比算法技巧
- 382浏览 收藏
-

- Golang · Go教程 | 47分钟前 |
- Golanggzip文件压缩与解压实现方法
- 144浏览 收藏
-

- Golang · Go教程 | 52分钟前 |
- Golang递归实现与尾递归优化详解
- 128浏览 收藏
-

- Golang · Go教程 | 56分钟前 |
- Golangtesting包使用教程与示例详解
- 340浏览 收藏
-

- Golang · Go教程 | 1小时前 |
- Golang接口指针能否用interface指针分析
- 408浏览 收藏
-

- Golang · Go教程 | 1小时前 |
- CentOS7升级Golang版本注意事项
- 314浏览 收藏
查看更多
课程推荐
-

- 前端进阶之JavaScript设计模式
- 设计模式是开发人员在软件开发过程中面临一般问题时的解决方案,代表了最佳的实践。本课程的主打内容包括JS常见设计模式以及具体应用场景,打造一站式知识长龙服务,适合有JS基础的同学学习。
- 543次学习
-

- GO语言核心编程课程
- 本课程采用真实案例,全面具体可落地,从理论到实践,一步一步将GO核心编程技术、编程思想、底层实现融会贯通,使学习者贴近时代脉搏,做IT互联网时代的弄潮儿。
- 516次学习
-

- 简单聊聊mysql8与网络通信
- 如有问题加微信:Le-studyg;在课程中,我们将首先介绍MySQL8的新特性,包括性能优化、安全增强、新数据类型等,帮助学生快速熟悉MySQL8的最新功能。接着,我们将深入解析MySQL的网络通信机制,包括协议、连接管理、数据传输等,让
- 500次学习
-

- JavaScript正则表达式基础与实战
- 在任何一门编程语言中,正则表达式,都是一项重要的知识,它提供了高效的字符串匹配与捕获机制,可以极大的简化程序设计。
- 487次学习
-

- 从零制作响应式网站—Grid布局
- 本系列教程将展示从零制作一个假想的网络科技公司官网,分为导航,轮播,关于我们,成功案例,服务流程,团队介绍,数据部分,公司动态,底部信息等内容区块。网站整体采用CSSGrid布局,支持响应式,有流畅过渡和展现动画。
- 485次学习
查看更多
AI推荐
-
- ChatExcel酷表
- ChatExcel酷表是由北京大学团队打造的Excel聊天机器人,用自然语言操控表格,简化数据处理,告别繁琐操作,提升工作效率!适用于学生、上班族及政府人员。
- 4104次使用
-
- Any绘本
- 探索Any绘本(anypicturebook.com/zh),一款开源免费的AI绘本创作工具,基于Google Gemini与Flux AI模型,让您轻松创作个性化绘本。适用于家庭、教育、创作等多种场景,零门槛,高自由度,技术透明,本地可控。
- 4453次使用
-
- 可赞AI
- 可赞AI,AI驱动的办公可视化智能工具,助您轻松实现文本与可视化元素高效转化。无论是智能文档生成、多格式文本解析,还是一键生成专业图表、脑图、知识卡片,可赞AI都能让信息处理更清晰高效。覆盖数据汇报、会议纪要、内容营销等全场景,大幅提升办公效率,降低专业门槛,是您提升工作效率的得力助手。
- 4340次使用
-

- 星月写作
- 星月写作是国内首款聚焦中文网络小说创作的AI辅助工具,解决网文作者从构思到变现的全流程痛点。AI扫榜、专属模板、全链路适配,助力新人快速上手,资深作者效率倍增。
- 5804次使用
-
- MagicLight
- MagicLight.ai是全球首款叙事驱动型AI动画视频创作平台,专注于解决从故事想法到完整动画的全流程痛点。它通过自研AI模型,保障角色、风格、场景高度一致性,让零动画经验者也能高效产出专业级叙事内容。广泛适用于独立创作者、动画工作室、教育机构及企业营销,助您轻松实现创意落地与商业化。
- 4699次使用
查看更多
相关文章
-
- Golangmap实践及实现原理解析
- 2022-12-28 505浏览
-
- go和golang的区别解析:帮你选择合适的编程语言
- 2023-12-29 503浏览
-
- 试了下Golang实现try catch的方法
- 2022-12-27 502浏览
-
- 如何在go语言中实现高并发的服务器架构
- 2023-08-27 502浏览
-
- 提升工作效率的Go语言项目开发经验分享
- 2023-11-03 502浏览




