七个流行的强化学习算法及代码实现
IT行业相对于一般传统行业,发展更新速度更快,一旦停止了学习,很快就会被行业所淘汰。所以我们需要踏踏实实的不断学习,精进自己的技术,尤其是初学者。今天golang学习网给大家整理了《七个流行的强化学习算法及代码实现》,聊聊,我们一起来看看吧!
目前流行的强化学习算法包括 Q-learning、SARSA、DDPG、A2C、PPO、DQN 和 TRPO。 这些算法已被用于在游戏、机器人和决策制定等各种应用中,并且这些流行的算法还在不断发展和改进,本文我们将对其做一个简单的介绍。
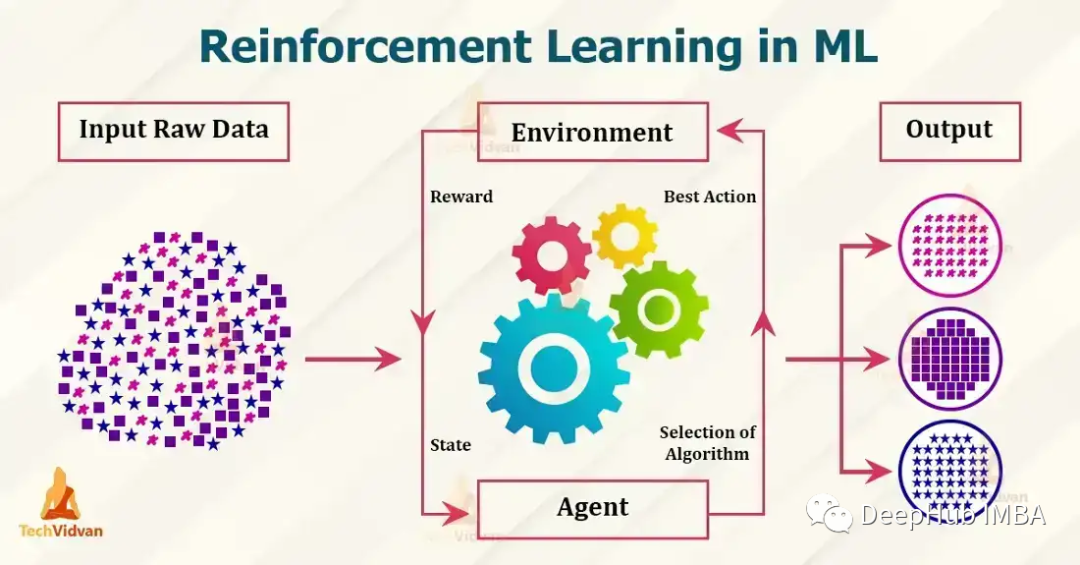
1、Q-learning
Q-learning:Q-learning 是一种无模型、非策略的强化学习算法。 它使用 Bellman 方程估计最佳动作值函数,该方程迭代地更新给定状态动作对的估计值。 Q-learning 以其简单性和处理大型连续状态空间的能力而闻名。
下面是一个使用 Python 实现 Q-learning 的简单示例:
import numpy as np # Define the Q-table and the learning rate Q = np.zeros((state_space_size, action_space_size)) alpha = 0.1 # Define the exploration rate and discount factor epsilon = 0.1 gamma = 0.99 for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state while not done: # Choose an action using an epsilon-greedy policy if np.random.uniform(0, 1) <p>上面的示例中,state_space_size 和 action_space_size 分别是环境中的状态数和动作数。 num_episodes 是要为运行算法的轮次数。 initial_state 是环境的起始状态。 take_action(current_state, action) 是一个函数,它将当前状态和一个动作作为输入,并返回下一个状态、奖励和一个指示轮次是否完成的布尔值。</p><p>在 while 循环中,使用 epsilon-greedy 策略根据当前状态选择一个动作。 使用概率 epsilon选择一个随机动作,使用概率 1-epsilon选择对当前状态具有最高 Q 值的动作。</p><p>采取行动后,观察下一个状态和奖励,使用Bellman方程更新q。 并将当前状态更新为下一个状态。这只是 Q-learning 的一个简单示例,并未考虑 Q-table 的初始化和要解决的问题的具体细节。</p><h4 style="line-height: 1;">2、SARSA </h4><p> SARSA:SARSA 是一种无模型、基于策略的强化学习算法。 它也使用Bellman方程来估计动作价值函数,但它是基于下一个动作的期望值,而不是像 Q-learning 中的最优动作。 SARSA 以其处理随机动力学问题的能力而闻名。</p><pre class="brush:javascript;toolbar:false;">import numpy as np # Define the Q-table and the learning rate Q = np.zeros((state_space_size, action_space_size)) alpha = 0.1 # Define the exploration rate and discount factor epsilon = 0.1 gamma = 0.99 for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state action = epsilon_greedy_policy(epsilon, Q, current_state) while not done: # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Choose next action using epsilon-greedy policy next_action = epsilon_greedy_policy(epsilon, Q, next_state) # Update the Q-table using the Bellman equation Q[current_state, action] = Q[current_state, action] + alpha * (reward + gamma * Q[next_state, next_action] - Q[current_state, action]) current_state = next_state action = next_action
state_space_size和action_space_size分别是环境中的状态和操作的数量。num_episodes是您想要运行SARSA算法的轮次数。Initial_state是环境的初始状态。take_action(current_state, action)是一个将当前状态和作为操作输入的函数,并返回下一个状态、奖励和一个指示情节是否完成的布尔值。
在while循环中,使用在单独的函数epsilon_greedy_policy(epsilon, Q, current_state)中定义的epsilon-greedy策略来根据当前状态选择操作。使用概率 epsilon选择一个随机动作,使用概率 1-epsilon对当前状态具有最高 Q 值的动作。
上面与Q-learning相同,但是采取了一个行动后,在观察下一个状态和奖励时它然后使用贪心策略选择下一个行动。并使用Bellman方程更新q表。
3、DDPG
DDPG 是一种用于连续动作空间的无模型、非策略算法。 它是一种actor-critic算法,其中actor网络用于选择动作,而critic网络用于评估动作。 DDPG 对于机器人控制和其他连续控制任务特别有用。
import numpy as np from keras.models import Model, Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Input from keras.optimizers import Adam # Define the actor and critic models actor = Sequential() actor.add(Dense(32, input_dim=state_space_size, activation='relu')) actor.add(Dense(32, activation='relu')) actor.add(Dense(action_space_size, activation='tanh')) actor.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) critic = Sequential() critic.add(Dense(32, input_dim=state_space_size, activation='relu')) critic.add(Dense(32, activation='relu')) critic.add(Dense(1, activation='linear')) critic.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) # Define the replay buffer replay_buffer = [] # Define the exploration noise exploration_noise = OrnsteinUhlenbeckProcess(size=action_space_size, theta=0.15, mu=0, sigma=0.2) for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state while not done: # Select an action using the actor model and add exploration noise action = actor.predict(current_state)[0] + exploration_noise.sample() action = np.clip(action, -1, 1) # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Add the experience to the replay buffer replay_buffer.append((current_state, action, reward, next_state, done)) # Sample a batch of experiences from the replay buffer batch = sample(replay_buffer, batch_size) # Update the critic model states = np.array([x[0] for x in batch]) actions = np.array([x[1] for x in batch]) rewards = np.array([x[2] for x in batch]) next_states = np.array([x[3] for x in batch]) target_q_values = rewards + gamma * critic.predict(next_states) critic.train_on_batch(states, target_q_values) # Update the actor model action_gradients = np.array(critic.get_gradients(states, actions)) actor.train_on_batch(states, action_gradients) current_state = next_state
在本例中,state_space_size和action_space_size分别是环境中的状态和操作的数量。num_episodes是轮次数。Initial_state是环境的初始状态。Take_action (current_state, action)是一个函数,它接受当前状态和操作作为输入,并返回下一个操作。
4、A2C
A2C(Advantage Actor-Critic)是一种有策略的actor-critic算法,它使用Advantage函数来更新策略。 该算法实现简单,可以处理离散和连续的动作空间。
import numpy as np from keras.models import Model, Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Input from keras.optimizers import Adam from keras.utils import to_categorical # Define the actor and critic models state_input = Input(shape=(state_space_size,)) actor = Dense(32, activation='relu')(state_input) actor = Dense(32, activation='relu')(actor) actor = Dense(action_space_size, activation='softmax')(actor) actor_model = Model(inputs=state_input, outputs=actor) actor_model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) state_input = Input(shape=(state_space_size,)) critic = Dense(32, activation='relu')(state_input) critic = Dense(32, activation='relu')(critic) critic = Dense(1, activation='linear')(critic) critic_model = Model(inputs=state_input, outputs=critic) critic_model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state done = False while not done: # Select an action using the actor model and add exploration noise action_probs = actor_model.predict(np.array([current_state]))[0] action = np.random.choice(range(action_space_size), p=action_probs) # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Calculate the advantage target_value = critic_model.predict(np.array([next_state]))[0][0] advantage = reward + gamma * target_value - critic_model.predict(np.array([current_state]))[0][0] # Update the actor model action_one_hot = to_categorical(action, action_space_size) actor_model.train_on_batch(np.array([current_state]), advantage * action_one_hot) # Update the critic model critic_model.train_on_batch(np.array([current_state]), reward + gamma * target_value) current_state = next_state
在这个例子中,actor模型是一个神经网络,它有2个隐藏层,每个隐藏层有32个神经元,具有relu激活函数,输出层具有softmax激活函数。critic模型也是一个神经网络,它有2个隐含层,每层32个神经元,具有relu激活函数,输出层具有线性激活函数。
使用分类交叉熵损失函数训练actor模型,使用均方误差损失函数训练critic模型。动作是根据actor模型预测选择的,并添加了用于探索的噪声。
5、PPO
PPO(Proximal Policy Optimization)是一种策略算法,它使用信任域优化的方法来更新策略。 它在具有高维观察和连续动作空间的环境中特别有用。 PPO 以其稳定性和高样品效率而著称。
import numpy as np from keras.models import Model, Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Input from keras.optimizers import Adam # Define the policy model state_input = Input(shape=(state_space_size,)) policy = Dense(32, activation='relu')(state_input) policy = Dense(32, activation='relu')(policy) policy = Dense(action_space_size, activation='softmax')(policy) policy_model = Model(inputs=state_input, outputs=policy) # Define the value model value_model = Model(inputs=state_input, outputs=Dense(1, activation='linear')(policy)) # Define the optimizer optimizer = Adam(lr=0.001) for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state while not done: # Select an action using the policy model action_probs = policy_model.predict(np.array([current_state]))[0] action = np.random.choice(range(action_space_size), p=action_probs) # Take the action and observe the next state and reward next_state, reward, done = take_action(current_state, action) # Calculate the advantage target_value = value_model.predict(np.array([next_state]))[0][0] advantage = reward + gamma * target_value - value_model.predict(np.array([current_state]))[0][0] # Calculate the old and new policy probabilities old_policy_prob = action_probs[action] new_policy_prob = policy_model.predict(np.array([next_state]))[0][action] # Calculate the ratio and the surrogate loss ratio = new_policy_prob / old_policy_prob surrogate_loss = np.minimum(ratio * advantage, np.clip(ratio, 1 - epsilon, 1 + epsilon) * advantage) # Update the policy and value models policy_model.trainable_weights = value_model.trainable_weights policy_model.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss=-surrogate_loss) policy_model.train_on_batch(np.array([current_state]), np.array([action_one_hot])) value_model.train_on_batch(np.array([current_state]), reward + gamma * target_value) current_state = next_state
6、DQN
DQN(深度 Q 网络)是一种无模型、非策略算法,它使用神经网络来逼近 Q 函数。 DQN 特别适用于 Atari 游戏和其他类似问题,其中状态空间是高维的,并使用神经网络近似 Q 函数。
import numpy as np from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Input from keras.optimizers import Adam from collections import deque # Define the Q-network model model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(32, input_dim=state_space_size, activation='relu')) model.add(Dense(32, activation='relu')) model.add(Dense(action_space_size, activation='linear')) model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=Adam(lr=0.001)) # Define the replay buffer replay_buffer = deque(maxlen=replay_buffer_size) for episode in range(num_episodes): current_state = initial_state while not done: # Select an action using an epsilon-greedy policy if np.random.rand() <p>上面的代码,Q-network有2个隐藏层,每个隐藏层有32个神经元,使用relu激活函数。该网络使用均方误差损失函数和Adam优化器进行训练。</p><h4 style="line-height: 1;">7、TRPO</h4><p>TRPO (Trust Region Policy Optimization)是一种无模型的策略算法,它使用信任域优化方法来更新策略。 它在具有高维观察和连续动作空间的环境中特别有用。</p><p>TRPO 是一个复杂的算法,需要多个步骤和组件来实现。TRPO不是用几行代码就能实现的简单算法。</p><p>所以我们这里使用实现了TRPO的现有库,例如OpenAI Baselines,它提供了包括TRPO在内的各种预先实现的强化学习算法,。</p><p>要在OpenAI Baselines中使用TRPO,我们需要安装:</p><p></p><pre class="brush:plain;toolbar:false;">pip install baselines
然后可以使用baselines库中的trpo_mpi模块在你的环境中训练TRPO代理,这里有一个简单的例子:
import gym
from baselines.common.vec_env.dummy_vec_env import DummyVecEnv
from baselines.trpo_mpi import trpo_mpi
#Initialize the environment
env = gym.make("CartPole-v1")
env = DummyVecEnv([lambda: env])
# Define the policy network
policy_fn = mlp_policy
#Train the TRPO model
model = trpo_mpi.learn(env, policy_fn, max_iters=1000)我们使用Gym库初始化环境。然后定义策略网络,并调用TRPO模块中的learn()函数来训练模型。
还有许多其他库也提供了TRPO的实现,例如TensorFlow、PyTorch和RLLib。下面时一个使用TF 2.0实现的样例
import tensorflow as tf
import gym
# Define the policy network
class PolicyNetwork(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self):
super(PolicyNetwork, self).__init__()
self.dense1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='relu')
self.dense2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='relu')
self.dense3 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
def call(self, inputs):
x = self.dense1(inputs)
x = self.dense2(x)
x = self.dense3(x)
return x
# Initialize the environment
env = gym.make("CartPole-v1")
# Initialize the policy network
policy_network = PolicyNetwork()
# Define the optimizer
optimizer = tf.optimizers.Adam()
# Define the loss function
loss_fn = tf.losses.BinaryCrossentropy()
# Set the maximum number of iterations
max_iters = 1000
# Start the training loop
for i in range(max_iters):
# Sample an action from the policy network
action = tf.squeeze(tf.random.categorical(policy_network(observation), 1))
# Take a step in the environment
observation, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# Compute the loss
loss = loss_fn(reward, policy_network(observation))
# Compute the gradients
grads = tape.gradient(loss, policy_network.trainable_variables)
# Perform the update step
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, policy_network.trainable_variables))
if done:
# Reset the environment
observation = env.reset()在这个例子中,我们首先使用TensorFlow的Keras API定义一个策略网络。然后使用Gym库和策略网络初始化环境。然后定义用于训练策略网络的优化器和损失函数。
在训练循环中,从策略网络中采样一个动作,在环境中前进一步,然后使用TensorFlow的GradientTape计算损失和梯度。然后我们使用优化器执行更新步骤。
这是一个简单的例子,只展示了如何在TensorFlow 2.0中实现TRPO。TRPO是一个非常复杂的算法,这个例子没有涵盖所有的细节,但它是试验TRPO的一个很好的起点。
总结
以上就是我们总结的7个常用的强化学习算法,这些算法并不相互排斥,通常与其他技术(如值函数逼近、基于模型的方法和集成方法)结合使用,可以获得更好的结果。
本篇关于《七个流行的强化学习算法及代码实现》的介绍就到此结束啦,但是学无止境,想要了解学习更多关于科技周边的相关知识,请关注golang学习网公众号!
 警惕!ChatGPT爆火下的能耗危机,数据中心运营商挑战巨大
警惕!ChatGPT爆火下的能耗危机,数据中心运营商挑战巨大
- 上一篇
- 警惕!ChatGPT爆火下的能耗危机,数据中心运营商挑战巨大
- 下一篇
- 深入浅出,解析ChatGPT背后的工作原理
-

- 科技周边 · 人工智能 | 2小时前 |
- ChatGPT在线入口,免费AI功能体验
- 264浏览 收藏
-

- 科技周边 · 人工智能 | 3小时前 |
- 豆包AI如何高效撰写精简周报
- 275浏览 收藏
-

- 科技周边 · 人工智能 | 3小时前 |
- Clawdbot账号被锁怎么解封?申诉教程
- 120浏览 收藏
-

- 科技周边 · 人工智能 | 3小时前 |
- Krikey.ai动作不自然怎么调?平滑技巧分享
- 152浏览 收藏
-

- 科技周边 · 人工智能 | 3小时前 |
- Clawdbot在新闻业的用途:事实核查指南
- 121浏览 收藏
-

- 科技周边 · 人工智能 | 3小时前 |
- 笔尖AIAPI接入教程与安全须知
- 321浏览 收藏
-

- 科技周边 · 人工智能 | 3小时前 |
- 豆包清空记录方法豆包一键清除聊天教程
- 225浏览 收藏
-

- 科技周边 · 人工智能 | 4小时前 |
- DeepSeek本地部署教程,Ollama安装详解
- 466浏览 收藏
-

- 科技周边 · 人工智能 | 4小时前 |
- Playwriter开源AI,人机协作更高效
- 485浏览 收藏
-

- 科技周边 · 人工智能 | 4小时前 |
- 关闭豆包AI自动联想设置步骤详解
- 130浏览 收藏
-

- 科技周边 · 人工智能 | 4小时前 |
- Claude官网入口及网页版使用指南
- 430浏览 收藏
-

- 前端进阶之JavaScript设计模式
- 设计模式是开发人员在软件开发过程中面临一般问题时的解决方案,代表了最佳的实践。本课程的主打内容包括JS常见设计模式以及具体应用场景,打造一站式知识长龙服务,适合有JS基础的同学学习。
- 543次学习
-

- GO语言核心编程课程
- 本课程采用真实案例,全面具体可落地,从理论到实践,一步一步将GO核心编程技术、编程思想、底层实现融会贯通,使学习者贴近时代脉搏,做IT互联网时代的弄潮儿。
- 516次学习
-

- 简单聊聊mysql8与网络通信
- 如有问题加微信:Le-studyg;在课程中,我们将首先介绍MySQL8的新特性,包括性能优化、安全增强、新数据类型等,帮助学生快速熟悉MySQL8的最新功能。接着,我们将深入解析MySQL的网络通信机制,包括协议、连接管理、数据传输等,让
- 500次学习
-

- JavaScript正则表达式基础与实战
- 在任何一门编程语言中,正则表达式,都是一项重要的知识,它提供了高效的字符串匹配与捕获机制,可以极大的简化程序设计。
- 487次学习
-

- 从零制作响应式网站—Grid布局
- 本系列教程将展示从零制作一个假想的网络科技公司官网,分为导航,轮播,关于我们,成功案例,服务流程,团队介绍,数据部分,公司动态,底部信息等内容区块。网站整体采用CSSGrid布局,支持响应式,有流畅过渡和展现动画。
- 485次学习
-
- ChatExcel酷表
- ChatExcel酷表是由北京大学团队打造的Excel聊天机器人,用自然语言操控表格,简化数据处理,告别繁琐操作,提升工作效率!适用于学生、上班族及政府人员。
- 4009次使用
-
- Any绘本
- 探索Any绘本(anypicturebook.com/zh),一款开源免费的AI绘本创作工具,基于Google Gemini与Flux AI模型,让您轻松创作个性化绘本。适用于家庭、教育、创作等多种场景,零门槛,高自由度,技术透明,本地可控。
- 4341次使用
-
- 可赞AI
- 可赞AI,AI驱动的办公可视化智能工具,助您轻松实现文本与可视化元素高效转化。无论是智能文档生成、多格式文本解析,还是一键生成专业图表、脑图、知识卡片,可赞AI都能让信息处理更清晰高效。覆盖数据汇报、会议纪要、内容营销等全场景,大幅提升办公效率,降低专业门槛,是您提升工作效率的得力助手。
- 4223次使用
-

- 星月写作
- 星月写作是国内首款聚焦中文网络小说创作的AI辅助工具,解决网文作者从构思到变现的全流程痛点。AI扫榜、专属模板、全链路适配,助力新人快速上手,资深作者效率倍增。
- 5518次使用
-
- MagicLight
- MagicLight.ai是全球首款叙事驱动型AI动画视频创作平台,专注于解决从故事想法到完整动画的全流程痛点。它通过自研AI模型,保障角色、风格、场景高度一致性,让零动画经验者也能高效产出专业级叙事内容。广泛适用于独立创作者、动画工作室、教育机构及企业营销,助您轻松实现创意落地与商业化。
- 4592次使用
-
- GPT-4王者加冕!读图做题性能炸天,凭自己就能考上斯坦福
- 2023-04-25 501浏览
-
- 单块V100训练模型提速72倍!尤洋团队新成果获AAAI 2023杰出论文奖
- 2023-04-24 501浏览
-
- ChatGPT 真的会接管世界吗?
- 2023-04-13 501浏览
-
- VR的终极形态是「假眼」?Neuralink前联合创始人掏出新产品:科学之眼!
- 2023-04-30 501浏览
-
- 实现实时制造可视性优势有哪些?
- 2023-04-15 501浏览





