mysql5.6主从搭建以及不同步问题详解
知识点掌握了,还需要不断练习才能熟练运用。下面golang学习网给大家带来一个数据库开发实战,手把手教大家学习《mysql5.6主从搭建以及不同步问题详解》,在实现功能的过程中也带大家重新温习相关知识点,温故而知新,回头看看说不定又有不一样的感悟!
系统:centos6.6
主:192.168.142.129 mysql-5.6.30.tar.gz
从:192.168.142.130 192.168.142.131 mysql-5.6.30.tar.gz
一、mysql主从复制原理
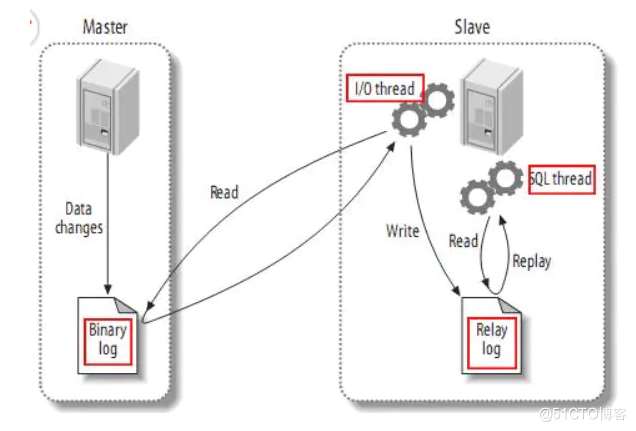
(1) master将改变记录到二进制日志(binary log)中;
(2) slave将master的binary log events拷贝到它的中继日志(relay log);slave的I/O线程从master的二进制日志中读取事件并写入中继日志;
(3) slave重做中继日志中的事件,将改变反映它自己的数据。slave的SQL线程从中继日志读取事件,并在本地重放其中的事件,使其与master中的数据一致。
mysql主从实现的步骤:
1、使用mysqldump 命令备份数据库,
2、查看主节点二进制的位置点
3、创建备份用户,并授权(replication client.replication slave)
4、从服务器修改server-id,必须与主mysql的server-id不同,开启中继日子,关闭二进制日子
5、从数据库,倒入数据,并使用授权用户,连接主mysql
6、start slave
SQL语言共分为以下几大类:查询语言DQL,控制语言DCL,操纵语言DML,定义语言DDL。事务控制TCL.
DQL(Data QUERY Languages)语句:即数据库定义语句,用来查询SELECT子句,FROM子句,WHERE子句组成的查询块,比如:select–from–where–grouop by–having–order by–limit
DDL(Data Definition Languages)语句:即数据库定义语句,用来创建数据库中的表、索引、视图、存储过程、触发器等,常用的语句关键字有CREATE,ALTER,DROP,TRUNCATE,COMMENT,RENAME。增删改表的结构
DML(Data Manipulation Language)语句:即数据操纵语句,用来查询、添加、更新、删除等,常用的语句关键字有:SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE,MERGE,CALL,EXPLAIN PLAN,LOCK TABLE,包括通用性的增删改查。增删改表的数据
DCL(Data Control Language)语句:即数据控制语句,用于授权/撤销数据库及其字段的权限(DCL is short name of Data Control Language which includes commands such as GRANT and mostly concerned with rights, permissions and other controls of the database system.)。常用的语句关键字有:GRANT,REVOKE。
TCL(Transaction Control Language)语句:事务控制语句,用于控制事务,常用的语句关键字有:COMMIT,ROLLBACK,SAVEPOINT,SET TRANSACTION。
二、mysql编译安装
#!/bin/bash
yum -y install make gcc gcc-c++ openssl openssl-devel pcre-devel gd cmake ncurses ncurses-devel
id -u mysql
if [ `echo $?` -ne 0 ];
then
groupadd mysql
useradd -M -g mysql -s /sbin/nologin mysql
fi
if [ ! -d "/usr/local/mysql" ];
then
mkdir -p /usr/local/mysql
fi
mkdir -p /data/mysql
chown -R mysql:mysql /data/mysql
cd /home/soft/ #软件存放目录
tar zxvf mysql-5.6.30.tar.gz
cd mysql-5.6.30
cmake -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local/mysql -DSYSCONFDIR=/etc -DMYSQL_DATADIR=/data/mysql/data -DINSTALL_MANDIR=/usr/share/man -DMYSQL_TCP_PORT=3306 -DMYSQL_UNIX_ADDR=/tmp/mysql.sock -DDEFAULT_CHARSET=utf8 -DEXTRA_CHARSETS=all -DDEFAULT_COLLATION=utf8_general_ci -DWITH_READLINE=1 -DWITH_SSL=system -DWITH_EMBEDDED_SERVER=1 -DENABLED_LOCAL_INFILE=1 -DWITH_INNOBASE_STORAGE_ENGINE=1
make && make install
chown -R mysql:mysql .
chmod +x scripts/mysql_install_db
./scripts/mysql_install_db --user=mysql --basedir=/usr/local/mysql --datadir=/data/mysql
cp ./support-files/mysql.server /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysqld
chmod 755 /etc/init.d/mysqld
chkconfig mysqld on
cat> /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysqld
# - Add the above to any other configuration file (for example ~/.my.ini)
# and copy my_print_defaults to /usr/bin
# - Add the path to the mysql-installation-directory to the basedir variable
# below.
#
# If you want to affect other MySQL variables, you should make your changes
# in the /etc/my.cnf, ~/.my.cnf or other MySQL configuration files.
# If you change base dir, you must also change datadir. These may get
# overwritten by settings in the MySQL configuration files.
basedir=/usr/local/mysql
datadir=/data/mysql
# Default value, in seconds, afterwhich the script should timeout waiting
# for server start.
# Value here is overriden by value in my.cnf.
# 0 means don't wait at all
# Negative numbers mean to wait indefinitely
service_startup_timeout=900
# Lock directory for RedHat / SuSE.
lockdir='/var/lock/subsys'
lock_file_path="$lockdir/mysql"
# The following variables are only set for letting mysql.server find things.
# Set some defaults
mysqld_pid_file_path=
if test -z "$basedir"
then
basedir=/usr/local/mysql
bindir=/usr/local/mysql/bin
if test -z "$datadir"
then
datadir=/data/mysql/data
fi
sbindir=/usr/local/mysql/bin
libexecdir=/usr/local/mysql/bin
else
bindir="$basedir/bin"
if test -z "$datadir"
then
datadir="$basedir/data"
fi
sbindir="$basedir/sbin"
libexecdir="$basedir/libexec"
fi
# datadir_set is used to determine if datadir was set (and so should be
# *not* set inside of the --basedir= handler.)
datadir_set=
# Use LSB init script functions for printing messages, if possible
#
lsb_functions="/lib/lsb/init-functions"
if test -f $lsb_functions ; then
. $lsb_functions
else
log_success_msg()
{
echo " SUCCESS! $@"
}
log_failure_msg()
{
echo " ERROR! $@"
}
fi
PATH="/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin:$basedir/bin"
export PATH
mode=$1 # start or stop
[ $# -ge 1 ] && shift
other_args="$*" # uncommon, but needed when called from an RPM upgrade action
# Expected: "--skip-networking --skip-grant-tables"
# They are not checked here, intentionally, as it is the resposibility
# of the "spec" file author to give correct arguments only.
case `echo "testing\c"`,`echo -n testing` in
*c*,-n*) echo_n= echo_c= ;;
*c*,*) echo_n=-n echo_c= ;;
*) echo_n= echo_c='\c' ;;
esac
parse_server_arguments() {
for arg do
case "$arg" in
--basedir=*) basedir=`echo "$arg" | sed -e 's/^[^=]*=//'`
bindir="$basedir/bin"
if test -z "$datadir_set"; then
datadir="$basedir/data"
fi
sbindir="$basedir/sbin"
libexecdir="$basedir/libexec"
;;
--datadir=*) datadir=`echo "$arg" | sed -e 's/^[^=]*=//'`
datadir_set=1
;;
--pid-file=*) mysqld_pid_file_path=`echo "$arg" | sed -e 's/^[^=]*=//'` ;;
--service-startup-timeout=*) service_startup_timeout=`echo "$arg" | sed -e 's/^[^=]*=//'` ;;
esac
done
}
wait_for_pid () {
verb="$1" # created | removed
pid="$2" # process ID of the program operating on the pid-file
pid_file_path="$3" # path to the PID file.
i=0
avoid_race_condition="by checking again"
while test $i -ne $service_startup_timeout ; do
case "$verb" in
'created')
# wait for a PID-file to pop into existence.
test -s "$pid_file_path" && i='' && break
;;
'removed')
# wait for this PID-file to disappear
test ! -s "$pid_file_path" && i='' && break
;;
*)
echo "wait_for_pid () usage: wait_for_pid created|removed pid pid_file_path"
exit 1
;;
esac
# if server isn't running, then pid-file will never be updated
if test -n "$pid"; then
if kill -0 "$pid" 2>/dev/null; then
: # the server still runs
else
# The server may have exited between the last pid-file check and now.
if test -n "$avoid_race_condition"; then
avoid_race_condition=""
continue # Check again.
fi
# there's nothing that will affect the file.
log_failure_msg "The server quit without updating PID file ($pid_file_path)."
return 1 # not waiting any more.
fi
fi
echo $echo_n ".$echo_c"
i=`expr $i + 1`
sleep 1
done
if test -z "$i" ; then
log_success_msg
return 0
else
log_failure_msg
return 1
fi
}
# Get arguments from the my.cnf file,
# the only group, which is read from now on is [mysqld]
if test -x ./bin/my_print_defaults
then
print_defaults="./bin/my_print_defaults"
elif test -x $bindir/my_print_defaults
then
print_defaults="$bindir/my_print_defaults"
elif test -x $bindir/mysql_print_defaults
then
print_defaults="$bindir/mysql_print_defaults"
else
# Try to find basedir in /etc/my.cnf
conf=/etc/my.cnf
print_defaults=
if test -r $conf
then
subpat='^[^=]*basedir[^=]*=\(.*\)$'
dirs=`sed -e "/$subpat/!d" -e 's//\1/' $conf`
for d in $dirs
do
d=`echo $d | sed -e 's/[ ]//g'`
if test -x "$d/bin/my_print_defaults"
then
print_defaults="$d/bin/my_print_defaults"
break
fi
if test -x "$d/bin/mysql_print_defaults"
then
print_defaults="$d/bin/mysql_print_defaults"
break
fi
done
fi
# Hope it's in the PATH ... but I doubt it
test -z "$print_defaults" && print_defaults="my_print_defaults"
fi
#
# Read defaults file from 'basedir'. If there is no defaults file there
# check if it's in the old (depricated) place (datadir) and read it from there
#
extra_args=""
if test -r "$basedir/my.cnf"
then
extra_args="-e $basedir/my.cnf"
else
if test -r "$datadir/my.cnf"
then
extra_args="-e $datadir/my.cnf"
fi
fi
parse_server_arguments `$print_defaults $extra_args mysqld server mysql_server mysql.server`
#
# Set pid file if not given
#
if test -z "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
then
mysqld_pid_file_path=$datadir/`hostname`.pid
else
case "$mysqld_pid_file_path" in
/* ) ;;
* ) mysqld_pid_file_path="$datadir/$mysqld_pid_file_path" ;;
esac
fi
case "$mode" in
'start')
# Start daemon
# Safeguard (relative paths, core dumps..)
cd $basedir
echo $echo_n "Starting MySQL"
if test -x $bindir/mysqld_safe
then
# Give extra arguments to mysqld with the my.cnf file. This script
# may be overwritten at next upgrade.
$bindir/mysqld_safe --datadir="$datadir" --pid-file="$mysqld_pid_file_path" $other_args >/dev/null 2>&1 &
wait_for_pid created "$!" "$mysqld_pid_file_path"; return_value=$?
# Make lock for RedHat / SuSE
if test -w "$lockdir"
then
touch "$lock_file_path"
fi
exit $return_value
else
log_failure_msg "Couldn't find MySQL server ($bindir/mysqld_safe)"
fi
;;
'stop')
# Stop daemon. We use a signal here to avoid having to know the
# root password.
if test -s "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
then
mysqld_pid=`cat "$mysqld_pid_file_path"`
if (kill -0 $mysqld_pid 2>/dev/null)
then
echo $echo_n "Shutting down MySQL"
kill $mysqld_pid
# mysqld should remove the pid file when it exits, so wait for it.
wait_for_pid removed "$mysqld_pid" "$mysqld_pid_file_path"; return_value=$?
else
log_failure_msg "MySQL server process #$mysqld_pid is not running!"
rm "$mysqld_pid_file_path"
fi
# Delete lock for RedHat / SuSE
if test -f "$lock_file_path"
then
rm -f "$lock_file_path"
fi
exit $return_value
else
log_failure_msg "MySQL server PID file could not be found!"
fi
;;
'restart')
# Stop the service and regardless of whether it was
# running or not, start it again.
if $0 stop $other_args; then
$0 start $other_args
else
log_failure_msg "Failed to stop running server, so refusing to try to start."
exit 1
fi
;;
'reload'|'force-reload')
if test -s "$mysqld_pid_file_path" ; then
read mysqld_pid /dev/null ; then
log_success_msg "MySQL running ($mysqld_pid)"
exit 0
else
log_failure_msg "MySQL is not running, but PID file exists"
exit 1
fi
else
# Try to find appropriate mysqld process
mysqld_pid=`pidof $libexecdir/mysqld`
if test -z $mysqld_pid ; then
if test -f "$lock_file_path" ; then
log_failure_msg "MySQL is not running, but lock file ($lock_file_path) exists"
exit 2
fi
log_failure_msg "MySQL is not running"
exit 3
else
log_failure_msg "MySQL is running but PID file could not be found"
exit 4
fi
fi
;;
*)
# usage
basename=`basename "$0"`
echo "Usage: $basename {start|stop|restart|reload|force-reload|status} [ MySQL server options ]"
exit 1
;;
esac
exit 0
EOF
cat> /etc/my.cnf > /etc/profile
sleep 2
source /etc/profile
service mysqld start
sleep 5
cd /usr/local/mysql/bin && mysqladmin -uroot password 'mysql' #授权root用户的password
source /etc/profile
三、主从配置
1、这里验证主库有数据的情况,然后授权有复制权限的用户
mysql> create database db1; mysql> use db1 mysql> create table t1(id int, name varchar(12)); mysql> insert into t1 values(1, 'tom'), (2, 'jerry'), (3, 'jack'); mysql> grant replication slave,replication client on *.* to 'backuser'@'192.168.142.130' identified by 'mysqll'; mysql> grant replication slave,replication client on *.* to 'backuser'@'192.168.142.131' identified by 'mysql'; mysql> flush privileges;
2、修改各个数据库的配置文件后重启数据库
vi /etc/my.cnf #主库配置文件 server-id=1 log-bin=mysql-bin binlog-do-db=db1 binlog-ignore-db=mysql vi /etc/my.cnf #从库配置文件 server-id=2 #从库id不能和主库一样,其他从库往后面排 log-bin=relay-bin replicate-do-db=db1 #同步db1库 replicate-ignore-db=mysql #不会同步mysql库 read_only #只读 service mysqld restart
3、主库锁表备份,然后文件传给从库
mysql> flush tables with read lock; #主库锁表防止新的数据写入 mysql> show master status; #查看主库位置节点 新打开一个终端备份: mysqldump -u root -p --default-character-set=utf8 --opt -Q -R --skip-lock-tables db1 > /root/db1.sql scp /root/db1.sql root@192.168.142.130:/root scp /root/db1.sql root@192.168.142.130:/root
4、从库导入数据,然后change到主库的节点
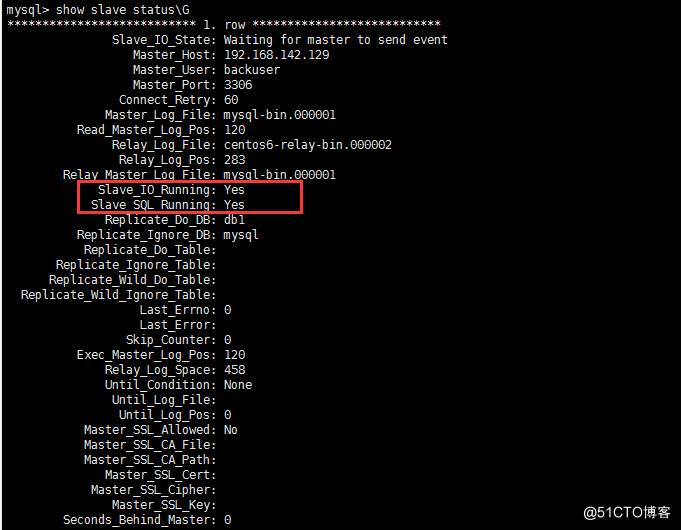
mysql -u root -p mysql> create database db1; mysql> use db1 mysql> source /root/db1.sql mysql> change master to master_host='192.168.142.129',master_user='backuser',master_password='mysql',master_log_file='mysql-bin.000001',master_log_pos=120; mysql> start slave; mysql> show slave status\G
5、主库解锁
mysql> unlock tables;
以上配置对主从不同步,重新配置主从同样适用。
四、主从不同步
1、造成不同步的原因
网络的延迟主从两台机器的负载不一致max_allowed_packet设置不一致key自增键开始的键值跟自增步长设置不一致引起的主从不一致mysql异常宕机情况下,如果未设置sync_binlog=1或者innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=1很有可能
出现binlog或者relaylog文件出现损坏,导致主从不一致mysql本身的bug引起的主从不同步版本不一致,特别是高版本是主,低版本为从的情况下,主数据库上面支持的功能,从数据库上面不支持该功能
2、解决办法
(1)忽略错误后,继续同步
该方法适用于主从库数据相差不大,或者要求数据可以不完全统一的情况,数据要求不严格的情况
stop slave; set global sql_slave_skip_counter =1; start slave; show slave status\G
(2)重新做主从
参考上面配置主库锁表重新做主从。
今天关于《mysql5.6主从搭建以及不同步问题详解》的内容介绍就到此结束,如果有什么疑问或者建议,可以在golang学习网公众号下多多回复交流;文中若有不正之处,也希望回复留言以告知!
 防止web项目中的SQL注入
防止web项目中的SQL注入
- 上一篇
- 防止web项目中的SQL注入
- 下一篇
- MySQL图形化管理工具Navicat安装步骤
-

- 数据库 · MySQL | 9小时前 |
- MySQL增删改查语法速查表大全
- 174浏览 收藏
-

- 数据库 · MySQL | 5天前 |
- MySQLupdate语句使用详解
- 120浏览 收藏
-

- 数据库 · MySQL | 1星期前 |
- MySQL数据库创建与字符集设置教程
- 404浏览 收藏
-

- 数据库 · MySQL | 1星期前 |
- MySQL基础命令速查:增删改查全攻略
- 427浏览 收藏
-

- 数据库 · MySQL | 2星期前 |
- MySQL优化Join查询的技巧与策略解析
- 351浏览 收藏
-

- 数据库 · MySQL | 2星期前 |
- MySQL常用数据类型有哪些及如何选择
- 156浏览 收藏
-

- 数据库 · MySQL | 3星期前 |
- MySQL增删改查语法速查手册
- 405浏览 收藏
-

- 数据库 · MySQL | 3星期前 |
- MySQLgroupby优化技巧与性能提升
- 497浏览 收藏
-

- 数据库 · MySQL | 3星期前 |
- MySQL读写分离方案与中间件解析
- 133浏览 收藏
-

- 数据库 · MySQL | 3星期前 |
- MySQL多方法批量插入数据技巧
- 319浏览 收藏
-

- 数据库 · MySQL | 3星期前 |
- MySQL排序优化与性能提升技巧
- 141浏览 收藏
-

- 数据库 · MySQL | 3星期前 |
- MySQL触发器应用场景及使用教程
- 256浏览 收藏
-

- 前端进阶之JavaScript设计模式
- 设计模式是开发人员在软件开发过程中面临一般问题时的解决方案,代表了最佳的实践。本课程的主打内容包括JS常见设计模式以及具体应用场景,打造一站式知识长龙服务,适合有JS基础的同学学习。
- 543次学习
-

- GO语言核心编程课程
- 本课程采用真实案例,全面具体可落地,从理论到实践,一步一步将GO核心编程技术、编程思想、底层实现融会贯通,使学习者贴近时代脉搏,做IT互联网时代的弄潮儿。
- 516次学习
-

- 简单聊聊mysql8与网络通信
- 如有问题加微信:Le-studyg;在课程中,我们将首先介绍MySQL8的新特性,包括性能优化、安全增强、新数据类型等,帮助学生快速熟悉MySQL8的最新功能。接着,我们将深入解析MySQL的网络通信机制,包括协议、连接管理、数据传输等,让
- 500次学习
-

- JavaScript正则表达式基础与实战
- 在任何一门编程语言中,正则表达式,都是一项重要的知识,它提供了高效的字符串匹配与捕获机制,可以极大的简化程序设计。
- 487次学习
-

- 从零制作响应式网站—Grid布局
- 本系列教程将展示从零制作一个假想的网络科技公司官网,分为导航,轮播,关于我们,成功案例,服务流程,团队介绍,数据部分,公司动态,底部信息等内容区块。网站整体采用CSSGrid布局,支持响应式,有流畅过渡和展现动画。
- 485次学习
-
- ChatExcel酷表
- ChatExcel酷表是由北京大学团队打造的Excel聊天机器人,用自然语言操控表格,简化数据处理,告别繁琐操作,提升工作效率!适用于学生、上班族及政府人员。
- 4110次使用
-
- Any绘本
- 探索Any绘本(anypicturebook.com/zh),一款开源免费的AI绘本创作工具,基于Google Gemini与Flux AI模型,让您轻松创作个性化绘本。适用于家庭、教育、创作等多种场景,零门槛,高自由度,技术透明,本地可控。
- 4454次使用
-
- 可赞AI
- 可赞AI,AI驱动的办公可视化智能工具,助您轻松实现文本与可视化元素高效转化。无论是智能文档生成、多格式文本解析,还是一键生成专业图表、脑图、知识卡片,可赞AI都能让信息处理更清晰高效。覆盖数据汇报、会议纪要、内容营销等全场景,大幅提升办公效率,降低专业门槛,是您提升工作效率的得力助手。
- 4343次使用
-

- 星月写作
- 星月写作是国内首款聚焦中文网络小说创作的AI辅助工具,解决网文作者从构思到变现的全流程痛点。AI扫榜、专属模板、全链路适配,助力新人快速上手,资深作者效率倍增。
- 5809次使用
-
- MagicLight
- MagicLight.ai是全球首款叙事驱动型AI动画视频创作平台,专注于解决从故事想法到完整动画的全流程痛点。它通过自研AI模型,保障角色、风格、场景高度一致性,让零动画经验者也能高效产出专业级叙事内容。广泛适用于独立创作者、动画工作室、教育机构及企业营销,助您轻松实现创意落地与商业化。
- 4700次使用
-
- 可能是最贴心的MySQL笔记了
- 2023-02-24 368浏览
-
- 一文详解MySQL主从同步原理
- 2022-12-30 371浏览
-
- MySQL的主从复制原理详细分析
- 2022-12-29 151浏览
-
- MySQL主从复制问题总结及排查过程
- 2022-12-28 437浏览
-
- MySQL 搭建主从同步实现操作
- 2023-01-07 117浏览




